“Ombudsmänner” is the German plural of “Ombudsmann,” meaning ombudsmen in English. Ombudsmen are independent officials who investigate complaints against institutions to promote fairness, transparency, accountability, and impartial dispute resolution.
Introduction
In modern societies, where institutions play an increasingly significant role in people’s daily lives, mechanisms for oversight and accountability are essential. One such mechanism is the ombudsman system, an office designed to investigate, mediate, and resolve complaints from individuals against powerful organizations or government bodies. In German, the plural form is “Ombudsmänner,” which directly translates to “ombudsmen” in English. Rooted in a long history of mediation and advocacy for fairness, ombudsmen act as a neutral bridge between citizens and institutions.
What Is an Ombudsman?
An ombudsman is an independent authority appointed to handle complaints and concerns raised by individuals against organizations or institutions. Their primary responsibility is to:
- Investigate grievances impartially
- Ensure transparency and accountability
- Recommend solutions or corrective actions
Ombudsmen function as bridges between the public and institutions, ensuring that processes remain fair and that decisions are scrutinized.
Historical Origins of the Term
The word ombudsman traces back to Sweden, where it was first introduced in the early 19th century. The Swedish Parliament established the role of a Justitieombudsman in 1809 to oversee public administration. From there, the model spread internationally, inspiring governments and organizations worldwide to adopt the concept.
Key historical milestones include:
- 1809 (Sweden): First ombudsman established to monitor government agencies.
- 20th century: Countries like Finland, Denmark, and Norway introduced similar roles.
- Post World War II: Ombudsman institutions expanded into Commonwealth countries, Europe, and beyond.
- Today: Ombudsmen exist in diverse sectors, such as education, healthcare, finance, and corporate governance.
Why Ombudsmänner Are Important
In today’s complex society, individuals often find themselves powerless when dealing with large institutions. Ombudsmänner play a crucial role in:
- Balancing Power: Providing citizens with a trusted avenue to challenge decisions made by governments, corporations, or public organizations.
- Encouraging Good Governance: Serving as watchdogs to prevent corruption, negligence, and abuse of authority.
- Protecting Human Rights: Acting as defenders of individual rights when institutions fail to deliver justice.
Types of Ombudsmänner
The role of ombudsmen has expanded across multiple sectors. Common categories include:
- Government Ombudsman: Investigates public complaints against administrative bodies.
- Corporate Ombudsman: Handles workplace conflicts, ethical concerns, and employee rights within companies.
- University Ombudsman: Supports students and faculty in academic disputes.
- Financial Ombudsman: Resolves complaints involving banks, insurance, and other financial institutions.
Ombudsmänner in the German Context
In Germany, Ombudsmänner function across government, finance, media, and consumer protection. Parliamentary petitions committees handle citizen grievances, while independent ombuds offices ensure accountability in various sectors. Increasingly, the gender-neutral term Ombudsleute is preferred, reflecting inclusivity in modern German usage and highlighting the role’s importance in safeguarding fairness and rights.
Gendered Variants in German
Language reflects society’s values, and the German terms for ombudsmen illustrate ongoing debates about gender inclusivity.
- Ombudsmann: Traditional masculine singular form.
- Ombudsfrau: Female counterpart, highlighting representation.
- Ombudsmänner: Masculine plural form, historically standard.
- Ombudsleute: Neutral plural form, widely adopted in professional and academic contexts.
How Ombudsmänner Ensure Impartiality
Ombudsmänner ensure impartiality by maintaining independence from political or corporate influence, adhering to strict ethical codes, and safeguarding confidentiality. Their recommendations are unbiased, based solely on facts and fairness. Appointed through transparent processes, they serve as neutral mediators, protecting citizens’ rights while fostering accountability and trust in institutions.
Advantages of the Ombudsman System
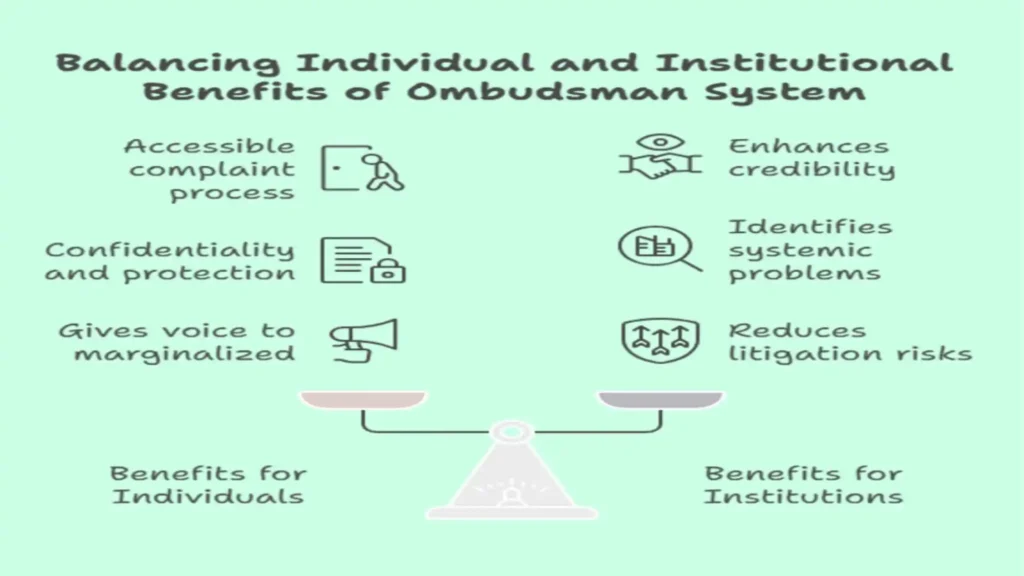
Challenges Facing Ombudsmänner
Despite their importance, ombudsmen face notable challenges:
- Limited Enforcement Power: Many can only recommend, not enforce, remedies.
- Resource Constraints: Small offices may struggle with caseloads.
- Public Awareness: Citizens are sometimes unaware of their right to use ombudsman services.
Global Perspective on Ombudsmen
Today, more than 120 countries have adopted some form of ombudsman institution. International organizations like the International Ombudsman Association (IOA) set global standards for ethics and practice.
Examples include:
- Sweden: The pioneer with the oldest parliamentary ombudsman system.
- United Kingdom: Financial Ombudsman Service and Parliamentary Ombudsman.
- United States: Corporate and university ombudsmen are widespread.
Future of Ombudsmänner
As society becomes increasingly digital and complex, the role of ombudsmen will continue to evolve.
- Digital Ombudsmen may oversee online platforms, AI ethics, and data privacy.
- International Collaboration will be essential for cross-border disputes.
The future suggests a stronger emphasis on inclusivity, transparency, and accountability, ensuring ombudsmen remain trusted guardians of fairness.
FAQs
Q1: Where did the word ombudsman originate?
It originates from Swedish, meaning “representative” or “agent.”
Q2: What is the gender-neutral term in German?
The gender-neutral plural is Ombudsleute, used instead of the male plural “Ombudsmänner.”
Conclusion
The concept of Ombudsmänner represents far more than a linguistic curiosity; it embodies a democratic safeguard. Rooted in Swedish history yet adapted into German and many other languages, the role of the ombudsman continues to evolve to meet modern demands for fairness, transparency, and accountability.

James Whitaker brings a wealth of knowledge and creativity to content writing across various niches such as health, technology, personal finance, and digital marketing. Known for his ability to simplify complex topics and deliver audience-centric content, he helps brands build authority and trust.

